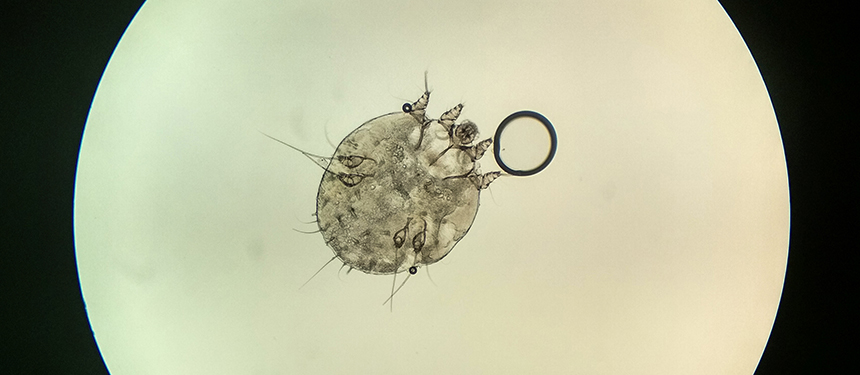
If you’re looking for a way to gross out your friends and family, show them can you see scabies with a magnifying glass. This little known fact is sure to impress (and gross out) anyone who hears it.
What is scabies?
Scabies is a skin condition that is caused by infestation with the human itch mite. The most common symptom of scabies is intense itching, which is often worse at night. Other symptoms may include a rash and bumps on the skin.
Scabies is spread by direct contact with an infested person. It can also be spread by sharing clothing or bedding with an infested person. Scabies is most commonly found in crowded areas, such as nursing homes, child care facilities, and prisons.
If you think you may have scabies, it is important to see a doctor for diagnosis and treatment. Scabies can be treated with medications that kill the mites. These medications are available by prescription from a doctor.
What are the symptoms of scabies?
Symptoms of scabies include intense itching and a pimple-like rash. The itching is usually worse at night. You may also have a rash of tiny red bumps, blisters or pus-filled bumps. This can happen 2 to 6 weeks after you’re infected.
If you’ve had scabies before, you may start to itch and get the rash within 1 to 4 days after being exposed again.
How is scabies transmitted?
Scabies is an itchy, highly contagious skin disease caused by the human itch mite. The mite burrows into the top layer of skin to live and lay its eggs. The most common symptom of scabies is intense itching, which is caused by an allergic reaction to the mites. Scabies is usually spread by direct, prolonged skin-to-skin contact with a person who has the disease. It can also be spread by sharing clothing or bedding with an infected person, or by contact with contaminated furniture, towels, or sheets.
How do you know if you have scabies?
There are several ways to know if you have scabies. The first way is to look for the telltale signs of scabies, which include intense itching, particularly at night; small, raised bumps on the skin; and thin lines on the skin called burrows. You can also look for these signs using a magnifying glass.
Another way to know if you have scabies is to have a skin scraping test performed by a doctor. This test involves taking a small sample of skin and looking at it under a microscope to see if there are any mites present.
If you think you might have scabies, it’s important to see a doctor so that you can get treatment. Scabies is very contagious and can spread quickly, so it’s important to get rid of the mites as soon as possible.
How do you treat scabies?
There are a number of ways to treat scabies, but the most common and effective method is to use a medicated cream or lotion that can be bought over the counter or prescribed by a doctor.
This cream will kill the mites that cause scabies, as well as their eggs. It is important to follow the instructions on the packet carefully, and to make sure that you cover all of the affected areas of skin.
The cream should be applied to clean, dry skin and left for 8-12 hours before being washed off. It may need to be used more than once to completely get rid of the mites.
In some cases, oral medication may also be prescribed.
Can you see scabies with a magnifying glass?
No, scabies cannot be seen with the naked eye. You will need a magnifying glass or microscope to see them.
What are the complications of scabies?
Although scabies is not generally considered a serious medical condition, it can cause a great deal of discomfort and can be difficult to treat. Left untreated, scabies can lead to serious complications, including:
-Bacterial skin infection. This is the most common complication of scabies. Bacteria can enter the skin through the Scabiei burrows, causing a red, crusted rash.
-Secondary bacterial skin infections can occur when people scratch their itch. This can lead to impetigo, cellulitis or folliculitis.
-Cellulitis is a bacterial infection that affects the skin and underlying tissues. It can cause redness, swelling and pain.
-Folliculitis is an infection of the hair follicles that can cause red bumps around the hair shafts.
-Impetigo is a highly contagious bacterial skin infection that causes sores and crusting on the skin.
How can you prevent scabies?
There is no one definitive answer to this question. However, some recommendations for preventing scabies include avoiding close contact with infected people, not sharing personal items such as towels or bedding with others, and washing bedding and clothing in hot water to kill any mites that may be present. Additionally, prompt treatment of any suspected cases of scabies is important in order to prevent the spread of the infestation.